Discover how pumps for hand sanitizer play a crucial role in efficient, safe sanitization processes. Hand sanitizer (antibacterial gel) has gone from a clinical specialty product to an everyday essential.
This surge in demand has driven the development of industrial solutions for sanitizer production, including specialized pumps and mixers. Q-Pumps®, a leader in sanitary industrial pumps, offers products like the QDB Series dry blender/mixer engineered for viscous gels such as hand sanitizer. These sanitary mixers and pumps ensure that gels are mixed, filled, and handled cleanly and reliably.
The Rise of Hand Sanitizer and Pump Technology
In recent years, hand sanitizer has become ubiquitous beyond hospitals and clinics. Shopping malls, offices, schools and homes all now require sanitizer on demand. This growth in use has spurred investments in production equipment, especially pumps for hand sanitizer, to meet the hygiene needs of society. Modern industrial pumps are designed to meet strict hygienic standards (3-A and EHEDG) and handle the thick, sticky nature of sanitizer gels. For example, Q-Pumps’ QDB Series is a modular inline mixer/blender with a sanitary design that makes it ideal for dissolving, mixing, and pumping viscous products like hand sanitizer
Pumps and mixers help combine ingredients (such as alcohol, glycerin and hydrogen peroxide) into a uniform gel while minimizing contamination. In many systems, pumps feed and circulate the mixture, and specialized valves prevent clogging. Q-Pumps’ mixers can even be converted to high-viscosity applications by adding a QTS twin-screw pump. These technologies ensure that hand sanitizer production is both efficient and compliant with food/pharma hygiene rules
What Is the Origin of Hand Sanitizer?
The concept of alcohol-based hand rubs dates back to the 1960s. In 1966, a nursing student named Guadalupe “Lupe” Hernández in California realized that hospital staff needed a way to sanitize hands between patients without constant handwashing. She devised an alcohol-based formula that effectively killed bacteria on contact. This led to the first commercial preparations of antibacterial hand gel, the most famous early brand being Purell in the 1980s.
Hand sanitizer gel was initially confined to healthcare settings, but its potential for preventing infection quickly became apparent. Over the decades, manufacturers refined the formula and distribution (pump bottles, dispensers) to make it practical for everyday use. Today, a wide range of formulations exist, often meeting guidelines from health authorities.
Impact of Pandemics on Hand Sanitizer
Global health events have dramatically increased hand sanitizer use. During the H1N1 flu pandemic of 2009, and especially the COVID-19 pandemic starting in 2020, sanitizer became essential. Demand surged, straining supply chains and highlighting the need for large-scale industrial production. Organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) strongly recommended using alcohol gels (with at least 60% alcohol) as an effective barrier against viruses and bacteria
As public reliance on sanitizers grew, manufacturers expanded capacity and adopted better pumping and mixing equipment. Efficient pumps and mixers became critical to rapidly scale up production while maintaining product quality. In fact, WHO issued hand sanitizer formulation guides and encouraged local manufacturing, which often involved industrial pumps in the mixing process. The result is a boom in pump technology tailored for hand sanitizer gel and similar products
Types of Hand Sanitizer and Their Uses
Hand sanitizers come in various formulations, each suited to different needs. Common types include:
- Broad-Spectrum Alcohol Gel. Kills a wide range of germs (viruses, bacteria, fungi). Ideal for hospital and healthcare environments where comprehensive disinfection is needed.
- Triclocarban-Based Gel. Contains triclocarban, an antimicrobial that disrupts bacterial cell membranes. Effective in clinical and medical settings.
- Triclosan-Based Gel. Uses triclosan, which affects microorganism cell walls. Regulatory agencies are restricting this due to environmental concerns.
- Citrus-Extract Gel. Uses natural citrus extracts with antimicrobial properties. Often marketed as more “natural” sanitizer.
- Chlorhexidine Gel. Contains chlorhexidine for a broad spectrum of action, especially used in surgeries and medical procedures for its strong antiseptic qualities.
- Alcohol-Based Gel (Ethyl, Isopropyl). The most common type. Contains 60–70% alcohol and effectively kills bacteria, viruses (including COVID-19 virus), and spores on the skin.
Each formulation has specific applications. For example, chlorhexidine and triclosan formulas are common in hospitals, while simple alcohol gels are used widely in consumer markets. Regardless of type, the production process typically involves blending alcohol and other ingredients into a consistent gel.
Recommendations for Hand Sanitizer
The World Health Organization has provided guidelines for making hand sanitizer, especially important during pandemic shortages. Key reasons WHO recommend alcohol-based hand rubs include:
- Broad Spectrum of Action. Effective against a wide variety of pathogens (viruses, bacteria) when formulated with sufficient alcohol.
- Accessibility. Can be used in locations where water and soap may not be readily available.
- Proven Efficacy. Studies show alcohol gels reduce infection risk and maintain sanitation with frequent use.
- Improved Hygiene Habits. Availability encourages hand hygiene compliance in healthcare and public settings.
- User Safety. When properly formulated (with emollients), they have low risk of skin irritation or other adverse reactions.
These advantages have driven the acceptance of hand sanitizer as a complementary sanitation method. Industrial equipment manufacturers like Q-Pumps have supported this by designing pumps and systems that safely handle the high alcohol content and ensure product consistency.
How Is Hand Sanitizer Made?
A standard WHO-recommended hand sanitizer formula includes:
- 96% Ethanol (denatured alcohol) – main antiseptic component.
- 3% Hydrogen Peroxide – helps eliminate contaminating bacteria in the solution.
- 98% Glycerol (glycerine) – a humectant that keeps the skin from drying out.
- Sterile Distilled or Boiled (then cooled) Water – diluent to reach the final volume.
These ingredients are mixed in precise proportions to create a gel that is both effective and comfortable to use. The general manufacturing steps are:
- Mix Alcohol and Hydrogen Peroxide. The alcohol (and propanol/isopropanol if used) is combined first with hydrogen peroxide to ensure a sterile solution.
- Add Glycerol. Glycerol is very viscous, so it must be pumped in carefully. Industrial pumps designed for high-viscosity fluids are crucial here to ensure uniform blending without air pockets.
- Add Water. The remaining volume is made up with sterile water while stirring the mixture.
- Seal or Cover Quickly. To prevent alcohol evaporation, the container (mixing tank) is sealed or covered immediately after mixing.
- Gentle Agitation. The solution is gently mixed to ensure homogeneity.
- Fill into Dispensers. Finally, the gel is pumped into individual bottles or dispensers for distribution.
Throughout this process, pumps and mixers must be sanitary (easy to clean) and capable of handling flammable liquids (alcohol) safely. For instance, Q-Pumps’ mixers and pumps use stainless steel with special seals to cope with alcohol-based fluids
Optimizing the manufacturing process with the right equipment is key. Q-Pumps offers expert advice and pump solutions tailored to hand sanitizer production. For example, Q-Pumps’ engineers can help choose the proper pump type (e.g., positive displacement vs. centrifugal) and configuration to handle the viscous gel and chemicals safely.
Request a Free Consultation to improve your gel production process.
Pumps for Hand Sanitizer: Q-Pumps Solutions
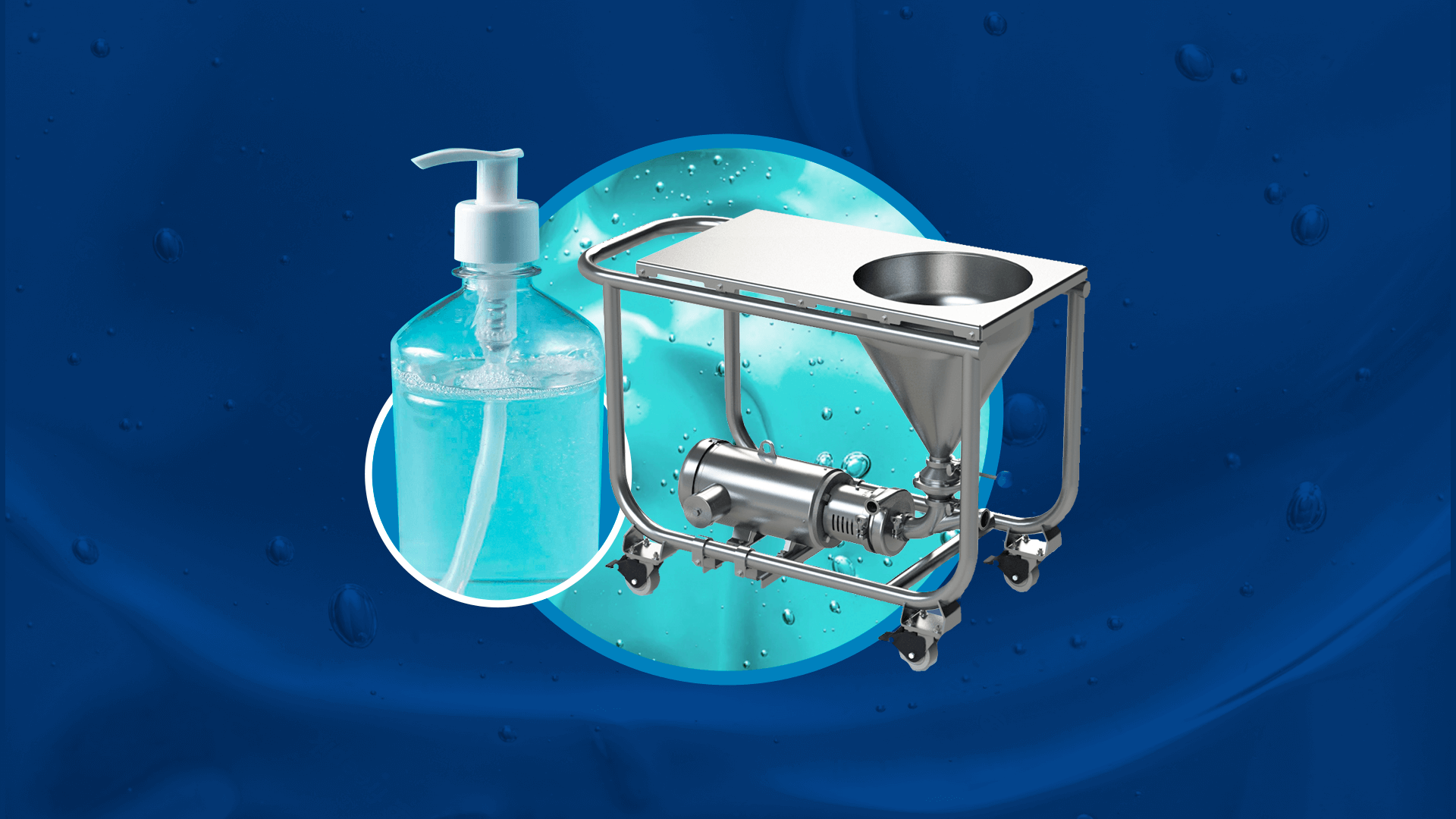
Q-Pumps has developed specialized equipment for hand sanitizer production. Chief among them is the QDB Series Dry Blender – a sanitary wet mixer designed for viscous gels. The QDB mixer combines an inline impeller (QIM mixer) with a sloped mixing table (cone) that simplifies adding powders or viscous ingredients. Its hygienic design (stainless steel, easy-to-clean surfaces) ensures that the hand sanitizer meets strict sanitary standards during mixing and pumping.
Key Features of the QDB Series:
- Sanitary Construction. All parts in contact with the product are polished stainless steel, meeting 3-A and EHEDG standards for food/pharma safety. Components like ball valves and seals are chosen to prevent contamination.
- Integrated Mixing Table and Cone. The sloped mixing table with built-in agitators allows powders (like thickening agents) to dissolve smoothly, without manual stirring. This is ideal when adding glycerol or other viscous components.
- Interchangeable Mixing Tools. Depending on formulation, different impeller or stirrer attachments can be used. The mixer can be customized for the ingredients’ characteristics (particle size, viscosity).
- Ball Valve and Clogging Prevention. A large ball valve allows dense materials and even granular additives to pass through without clogging. This design prevents build-up and simplifies cleaning.
- Modular Pump Integration. The QDB system can be combined with other Q-Pumps products. For example, adding a QTS twin-screw pump can convert the QDB into a high-viscosity pumping system (the QVM Visco Mixer) for very thick gels. Q-Pumps also offers centrifugal and lobe pumps (QC, QL series) that can feed or discharge the mixed sanitizer into filling lines.
- Optional Seals and Configurations. Standard silicon-carbide (SiC/SiC) mechanical seals are available for high durability against alcohol. Upgraded seal options are offered for extra safety. The mixer can also be converted into other configurations (inline mixing QIM) for different plant layouts.
All these features make the QDB mixer a turnkey solution for gel sanitizers. In use, a QDB unit will mix the alcohol, glycerin, and water to a perfect gel consistency, ready for pumping into bottles. The integrated valves and easy-clean design ensure minimal downtime between batches, which is crucial for high-demand production lines.
Learn more about the advantages of the QDB Series on the Q-Pumps website You can find details on the QDB dry blender here: QDB Series (Dry Blender) (Spanish page).
Sanitary Certifications of the QDB Pump
Sanitary compliance is critical in any hand sanitizer manufacturing line. The QDB and related Q-Pumps equipment meet all major international food/pharma hygiene standards:
- 3-A Sanitary Standards
Q-Pumps holds 3-A certificates 1004 and 1805, ensuring that the design of QDB mixers meets the stringent cleanliness requirements for food, beverage, and pharmaceutical processing. This means all surfaces are accessible for cleaning and there are no pockets where product can accumulate.
- EHEDG (European Hygienic Engineering & Design Group)
The QDB Series is EHEDG-certified, a European standard that validates hygienic design in equipment for food production EHEDG certification guarantees that the mixer’s construction prevents microbial contamination during processing and cleaning.
By using certified equipment like the QDB mixer, manufacturers gain confidence that their sanitizer batches are produced under sanitary conditions. As Q-Pumps states, “the QDB pump complies with the highest hygiene standards” and meets both 3-A and EHEDG requirements. Choosing certified pumps and mixers is an investment in quality assurance and regulatory compliance.
Gaining trust with sanitary pumps also strengthens your brand. Q-Pumps is a recognized leader in sanitary pump technology; their website provides more information on these standards and how Q-Pumps meet them
Q-Pumps: Your Partner in Pharmaceutical and Sanitizer Industries
Hand sanitizer has forever changed hygiene standards, and its industrial production demands cutting-edge technology. Pumps for hand sanitizer, like the QDB Series from Q-Pumps®, enable not only safe and efficient production but also flexibility and scalability for different formulations. By selecting the right mix of pumps and mixers – whether it’s the QDB dry blender for gel mixing, QTS pumps for viscous transfers, or centrifugal pumps for transfer lines – companies can ensure high output and consistency.
Contact us today to take your manufacturing to the next level!